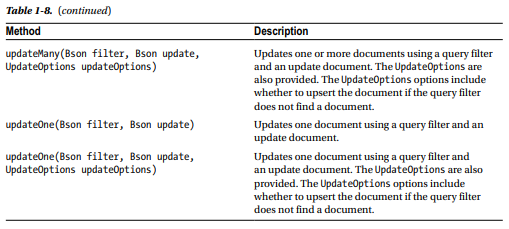
In this section we shall update MongoDB data. We shall be using the UpdateDBDocument application. The MongoCollection<TDocument> class provides several methods, some of them overloaded, to find and update data as discussed in Table 1-8.

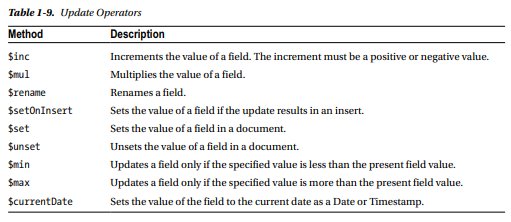
Some of the methods listed support only update operators in the update document. The update operators that may be applied on document fields are discussed in Table 1-9.
- In the UpdateDBDocument application create a MongoClient instance as discussed earlier and create a MongoDatabase instance for the local database. Subsequently, create a MongoCollection<TDocument> instance for the catalog collection. Add two instances of Catalog objects to the catalog collection using the insertOne(TDocument document) method.
Document catalog = new Document(“catalogId”, “catalog1”)
.append(“journal”, “Oracle Magazine”)
.append(“publisher”, “Oracle Publishing”)
.append(“edition”, “November December 2013”)
.append(“title”, “Engineering as a Service”)
.append(“author”, “David A. Kelly”);
coll.insertOne(catalog);
catalog = new Document(“catalogId”, “catalog2”)
.append(“journal”, “Oracle Magazine”)
.append(“publisher”, “Oracle Publishing”)
.append(“edition”, “November December 2013”)
.append(“title”, “Quintessential and Collaborative”)
.append(“author”, “Tom Haunert”);
coll.insertOne(catalog);
- As an example of using the updateOne(Bson filter, Bson update) method, update the edition and author fields of the Document instance with catalogId catalog1 using the update operator $set.
coll.updateOne(new Document(“catalogId”, “catalog1”),new Document(“$set”, new
Document(“edition”, “11-12 2013”).append(“author”, “Kelly, David A.”)));
- As an example of using the updateMany(Bson filter, Bson update) method, update the journal field of all Document instances using update operator $set.
coll.updateMany(new Document(“journal”, “Oracle Magazine”),
new Document(“$set”, new Document(“journal”, “OracleMagazine”)));
- As an example of using the replaceOne(Bson filter, TDocument replacement, UpdateOptions updateOptions) method, replace the Document instance with catalogId catalog3, which does not exist, with a new Document instance. Provide an UpdateOptions argument to upsert the Document if the query filter does not return a Document instance.
UpdateResult result = coll.replaceOne(new Document(“catalogId”,
“catalog3”),new Document(“catalogId”, “catalog3”).append(“journal”,
“Oracle Magazine”).append(“publisher”, “Oracle Publishing”).
append(“edition”, “November December 2013”).append(“title”,
“Engineering as a Service”).append(“author”, “David A. Kelly”),
new UpdateOptions().upsert(true));
- The replaceOne() method returns an UpdateResult object. Output the following:
- The number of documents matched using the getMatchedCount() method of UpdateResult.
- The number of documents modified using the getModifiedCount() method.
Not all matched documents may be modified.
- The _id field value for the upserted document using the getUpsertedId() method. The _id field value has to be obtained using the asObjectId() method invocation followed by the getValue() method invocation.
System.out.println(“Number of documents matched: “+ result.getMatchedCount());
System.out.println(“Number of documents modified: “+ result.getModifiedCount());
System.out.println(“Upserted Document Id: “+ result.getUpsertedId().asObjectId(). getValue());
- To verify that the documents got updated or replaced, output all the documents in the catalog collection. Create a FindIterable<TDocument> for the documents in the catalog collection using the find() method. Subsequently, use an enhanced for loop to obtain the Document instances and output the key/value pairs in each Document instance as discussed earlier.
The UpdateDBDocument application is listed below.
package mongodb;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import org.bson.Document;
import com.mongodb.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.ServerAddress;
import com.mongodb.client.FindIterable;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.client.model.UpdateOptions;
import com.mongodb.client.result.UpdateResult;
public class UpdateDBDocument {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MongoClient mongoClient = new MongoClient(
Arrays.asList(new ServerAddress(“localhost”, 27017)));
MongoDatabase db = mongoClient.getDatabase(“local”);
MongoCollection<Document> coll = db.getCollection(“catalog”);
Document catalog = new Document(“catalogId”, “catalog1”)
.append(“journal”, “Oracle Magazine”)
.append(“publisher”, “Oracle Publishing”)
.append(“edition”, “November December 2013”)
.append(“title”, “Engineering as a Service”)
.append(“author”, “David A. Kelly”);
coll.insertOne(catalog);
catalog = new Document(“catalogId”, “catalog2”)
.append(“journal”, “Oracle Magazine”)
.append(“publisher”, “Oracle Publishing”)
.append(“edition”, “November December 2013”)
.append(“title”, “Quintessential and Collaborative”)
.append(“author”, “Tom Haunert”);
coll.insertOne(catalog);
coll.updateOne(
new Document(“catalogId”, “catalog1”),
new Document(“$set”, new Document(“edition”, “11-12 2013”)
.append(“author”, “Kelly, David A.”)));
coll.updateMany(new Document(“journal”, “Oracle Magazine”),
new Document(“$set”, new Document(“journal”, “OracleMagazine”)));
UpdateResult result = coll.replaceOne(
new Document(“catalogId”, “catalog3”),
new Document(“catalogId”, “catalog3”)
.append(“journal”, “Oracle Magazine”)
.append(“publisher”, “Oracle Publishing”)
.append(“edition”, “November December 2013”)
.append(“title”, “Engineering as a Service”)
.append(“author”, “David A. Kelly”),
new UpdateOptions().upsert(true));
System.out.println(“Number of documents modified: “
+ result.getModifiedCount());
System.out.println(“Upserted Document Id: “
+ result.getUpsertedId().asObjectId().getValue());
FindIterable<Document> iterable = coll.find();
String documentKey = null;
for (Document document : iterable) {
Set<String> keySet = document.keySet();
Iterator<String> iter = keySet.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
documentKey = iter.next();
System.out.println(documentKey);
System.out.println(document.get(documentKey));
}
}
7. Again, before running the application drop the catalog collection with db.catalog.drop() command in mongo shell. To run the UpdateDBDocument.java application right-click on UpdateDBDocument.java in Package Explorer and select Run As ► Java Application as shown in Figure 1-17.
The output from the UpdateDBDocument.java application is as follows.
Number of documents matched: 0
Number of documents modified: 0
Upserted Document Id: 55d4e56c0bc271d4a7002749
_id
55d4e56cd292641a003cb55a
catalogId
catalog1
journal
OracleMagazine
publisher
Oracle Publishing
edition
11-12 2013
title
Engineering as a Service author
Kelly, David A.
_id
55d4e56cd292641a003cb55b
catalogId
catalog2
journal
OracleMagazine publisher Oracle Publishing edition
November December 2013 title
Quintessential and Collaborative
author
Tom Haunert
_id
55d4e56c0bc271d4a7002749
catalogId
catalog3
journal
Oracle Magazine publisher Oracle Publishing edition
November December 2013 title
Engineering as a Service author
David A. Kelly
The updateOne() method example updates the edition and author fields of the document with catalogId as catalog1 using the update operator $set. The updateMany() method example sets the journal field of all documents to OracleMagazine using the update operator $set. As indicated in the output, the number of documents matched and modified are both 0 for the replaceOne() method example. Because UpdateOptions are set to upsert a document, a new document gets added when a Document instance for catalogId catalog3 is not found.
Source: Vohra Deepak (2015), Pro MongoDB™ Development, Apress; 1st ed. edition.
