Git is an Open Source Distributed Version Control System. Now that’s a lot of words to define Git. Let me break it down and explain the wording:
- Control System: This basically means that Git is a content tracker. So Git can be used to store content — it is mostly used to store code due to the other features it provides.
- Version Control System: The code which is stored in Git keeps changing as more code is added. Also, many developers can add code in parallel. So Version Control System helps in handling this by maintaining a history of what changes have happened. Also, Git provides features like branches and merges, which I will be covering later.
- Distributed Version Control System: Git has a remote repository which is stored in a server and a local repository which is stored in the computer of each developer. This means that the code is not just stored in a central server, but the full copy of the code is present in all the developers’ computers. Git is a Distributed Version Control System since the code is present in every developer’s computer. I will explain the concept of remote and local repositories later in this article.
What Is Version Control?
Version control helps developers track and manage changes to a software project’s code. As a software project grows, version control becomes essential. Take WordPress…
At this point, WordPress is a pretty big project. If a core developer wanted to work on one specific part of the WordPress codebase, it wouldn’t be safe or efficient to have them directly edit the “official” source code.
Instead, version control lets developers safely work through branching and merging.
With branching, a developer duplicates part of the source code (called the repository). The developer can then safely make changes to that part of the code without affecting the rest of the project.
Then, once the developer gets his or her part of the code working properly, he or she can merge that code back into the main source code to make it official.
All of these changes are then tracked and can be reverted if need be.
Why a Version Control System like Git is needed
Real life projects generally have multiple developers working in parallel. So a version control system like Git is needed to ensure there are no code conflicts between the developers.
Additionally, the requirements in such projects change often. So a version control system allows developers to revert and go back to an older version of the code.
Finally, sometimes several projects which are being run in parallel involve the same codebase. In such a case, the concept of branching in Git is very important.
What Is Git?
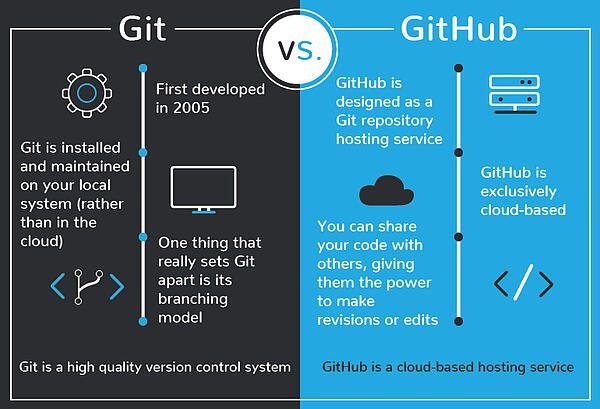
Git is a specific open-source version control system created by Linus Torvalds in 2005.
Specifically, Git is a distributed version control system, which means that the entire codebase and history is available on every developer’s computer, which allows for easy branching and merging.
According to a Stack Overflow developer survey, over 87% of developers use Git.
So What Is GitHub, Then?
GitHub is a for-profit company that offers a cloud-based Git repository hosting service. Essentially, it makes it a lot easier for individuals and teams to use Git for version control and collaboration.
GitHub’s interface is user-friendly enough so even novice coders can take advantage of Git. Without GitHub, using Git generally requires a bit more technical savvy and use of the command line.
GitHub is so user-friendly, though, that some people even use GitHub to manage other types of projects – like writing books.
Additionally, anyone can sign up and host a public code repository for free, which makes GitHub especially popular with open-source projects.
As a company, GitHub makes money by selling hosted private code repositories, as well as other business-focused plans that make it easier for organizations to manage team members and security. We utilize Github extensively at Kinsta to manage and develop internal projects.
Git vs. GitHub
Git or GitHub. Are they the same thing? If not, are they connected in some way? Or, like Java and JavaScript, is the connection only superficial?
These questions are definitely worth asking. After all, Microsoft was willing to shell out $7.5 billion dollars to acquire GitHub back in 2018, so developers of all skill levels should be sitting up and taking notice. But the truth is that Git and GitHub are connected much more closely than Java and JavaScript — but with some key differences setting them apart.
What’s the difference between Git and GitHub? Well, to answer that, we’ll be taking a closer look at each one. But before we do that, let’s first discuss the concept of version control.