There are various anomalies or pitfalls in relational database. Various dependencies in relational database cause these anomalies.
Anomalies : Anomalies refer to the undesirable results because of modification of data. Consider the relation Employee with attributes EID, Name, Salary, Dept.No, Dept.Name as shown in Figure 6.8. The various anomalies are as follows:
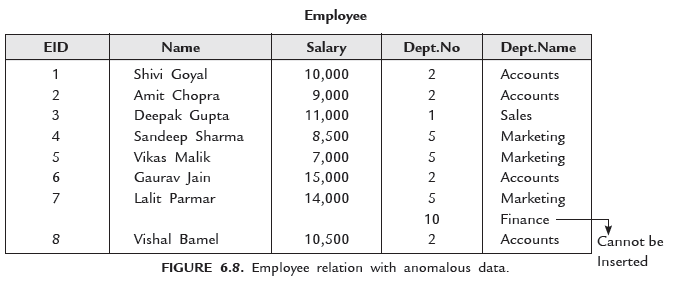
1. Insertion Anomaly
Suppose you want to add new information in any relation but cannot enter that data because of some constraints. This is known as Insertion anomaly. In relation Employee, you cannot add new department Finance unless there is an employee in Finance department. Addition of this information violates Entity Integrity Rule 1. (Primary Key cannot be NULL). In other words, when you depend on any other information to add new information then it leads to insertion anomaly.
2. Deletion Anomaly
The deletion anomaly occurs when you try to delete any existing information from any relation and this causes deletion of any other undesirable information.
In relation Employee, if you try to delete tuple containg Deepak this leads to the deletion of department “Sales” completely (there is only one employee in sales department).
3. Updation Anomaly
The updation anomaly occurs when you try to update any existing information in any relation and this causes inconsistency of data.
In relation Employee, if you change the Dept.No. of department Accounts.
Note: We can update only one tuple at a time.
This will cause inconsistency if you update Dept.No. of single employee only otherwise you have to search all employees working in Accounts department and update them individually.
Source: Gupta Satinder Bal, Mittal Aditya (2017), Introduction to Basic Database Management System, 2nd Edition-University Science Press (2017)
