SQL Server is a relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft. It is primarily designed and developed to compete with MySQL and Oracle database. SQL Server supports ANSI SQL, which is the standard SQL (Structured Query Language) language. However, SQL Server comes with its own implementation of the SQL language, T-SQL (Transact-SQL).
T-SQL is a Microsoft propriety Language known as Transact-SQL. It provides further capabilities of declaring variable, exception handling, stored procedure, etc.
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is the main interface tool for SQL Server, and it supports both 32-bit and 64-bit environments.
SQL Server Editions
Following are the popular editions/types of SQL server:
SQL Server Enterprise: It is used in the high end, large scale and mission Critical business. It provides High-end security, Advanced Analytics, Machine Learning, etc.
SQL Server Standard: Itis suitable for Mid-Tier Application and Data Marts. It includes basic reporting and analytics.
SQL Server WEB: It is designed for a low total-cost-of-ownership option for Web hosters. It provides scalability, affordability, and manageability capabilities for small to large scale Web properties.
SQL Server Developer: It is similar to an enterprise edition for the non-production environment. It is mainly used for build, test, and demo.
SQL Server Express: It is for small scale applications and free to use.
MS SQL Server as Client-Server Architecture
Let’s have a look at the below early morning conversation between Mom and her Son, Tom.
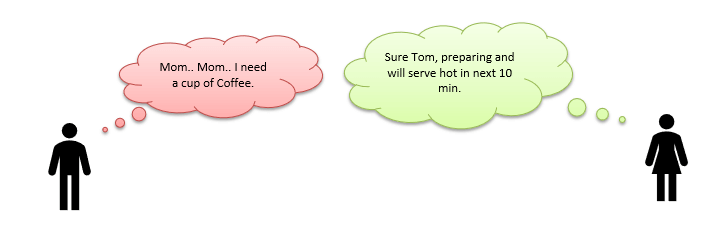
Brainstorm:
Ask your brain….!!! “Can you map, who is CLIENT and who the SERVER is?”
The most certain reply would be – “I am pretty smart in that and…. Son is a CLIENT as he is requesting for a cup of coffee and Mother, who is CAPABLE of preparing coffee, is a SERVER.”
Here, Tom is requesting his mother, a cup of coffee. Finally, mom does some processing with Milk, coffee, sugar and prepare coffee to serve it hot.
Analogy: MS SQL SERVER architecture.
A CLIENT is an application that sends requests to the MS SQL SERVER installed on a given machine. The SERVER is capable of processing input data as requested. Finally, respond with PROCESSED OUTPUT DATA as a result.
Key Components and Services of SQL Server
Below are the main components and services of SQL server:
Database Engine: This component handle storage, Rapid transaction Processing, and Securing Data.
SQL Server: This service starts, stops, pauses, and continues an instance of Microsoft SQL Server. Executable name is sqlservr.exe.
SQL Server Agent: It performs the role of Task Scheduler. It can be triggered by any event or as per demand. Executable name is sqlagent.exe.
SQL Server Browser: This listens to the incoming request and connects to the desired SQL server instance. Executable name is sqlbrowser.exe.
SQL Server Full-Text Search: This lets user running full-text queries against Character data in SQL Tables.Executable name is fdlauncher.exe.
SQL Server VSS Writer: This allows backup and restoration of data files when the SQL server is not running.Executable name is sqlwriter.exe.
SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS): Provide Data analysis, Data mining and Machine Learning capabilities. SQL server is integrated with R and Python language for advanced analytics. Executable name is msmdsrv.exe.
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS): Provides reporting features and decision-making capabilities. It includes integration with Hadoop. Executable name is ReportingServicesService.exe.
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS): Provided Extract-Transform and Load capabilities of the different type of data from one source to another. It can be view as converting raw information into useful information. Executable name is MsDtsSrvr.exe.
SQL Server Instances
SQL Server allows you to run multiple services at a go, with each service having separate logins, ports, databases, etc. These are divided into two:
- Primary Instances
- Named Instances
There are two ways through which we may access the primary instance. First, we can use the server name. Secondly, we can use its IP address. Named instances are accessed by appending a backslash and instance name.
For example, to connect to an instance named xyx on the local server, you should use 127.0.0.1\xyz. From SQL Server 2005 and above, you are allowed to run up to 50 instances simultaneously on a server.
Note that even though you can have multiple instances on the same server, only one of them must be the default instance while the rest must be named instances. One can run all the instances concurrently, and each instance runs independent of the other instances.
Importance of SQL Server Instances
The following are the advantages of SQL Server instances:
1. For installation of different versions on one machine You can have different versions of SQL Server on a single machine. Each installation works independently from the other installations.
2. For cost reduction: Instances can help us reduce the costs of operating SQL Server, especially in purchasing the SQL Server license. You can get different services from different instances, hence no need for purchasing one license for all services.
3. For maintenance of development, production and test environments separately: This is the main benefit of having many SQL Server instances on a single machine. You can use different instances for development, production and test purposes.
4. For reducing temporary database problems: When you have all services running on a single SQL Server instance, there are high chances of having problems with the problems, especially problems that keep on recurring. When such services are run on different instances, you can avoid having such problems.
5. For separating security privileges: When different services are running on different SQL Server instances, you can focus on securing the instance running the most sensitive service.
6. For maintaining a standby server: A SQL Server instance can fail, leading to an outage of services. This explains the importance of having a standby server to be brought in if the current server fails. This can easily be achieved using SQL Server instances.
